二叉树
二叉树定义
A binary tree is a restriction where each node has exactly two children:
- Each child is either empty or another binary tree
- This restriction allows us to label the children as left and right subtrees
二叉树分类
perfect binary tree
定义
一个二叉树是完美二叉树,它必须满足如下的要求
- All leaf nodes have the same depth
- All other nodes are full
性质
常用的五条定理
- A perfect binary tree of height $h$ has $2^{h + 1} – 1$ nodes
- The height is $\Theta(\ln(n))$
- There are $2^h$ leaf nodes
- The average depth of a node is $\Theta(\ln(n))$
其中,第四条难以直接看出,这里提供一个简要的证明:
$$
\frac{\sum\limits_{k=0}^hk2^k}{2^{h+1}-1}=\frac{h2^{h+1}-2^{h+1}+2}{2^{h+1}-1}=h-1+\frac{h+1}{2^{h+1}-1}\approx h-1 = \Theta(\ln(n))
$$
complete binary tree
定义
a complete binary tree of height $h$ is a tree where either
- The left sub-tree is a complete tree of height h – 1 and the right subtree is a perfect tree of height h – 2, or
- The left sub-tree is perfect tree with height h – 1 and the right sub-tree is complete tree with height h – 1
示例图如下
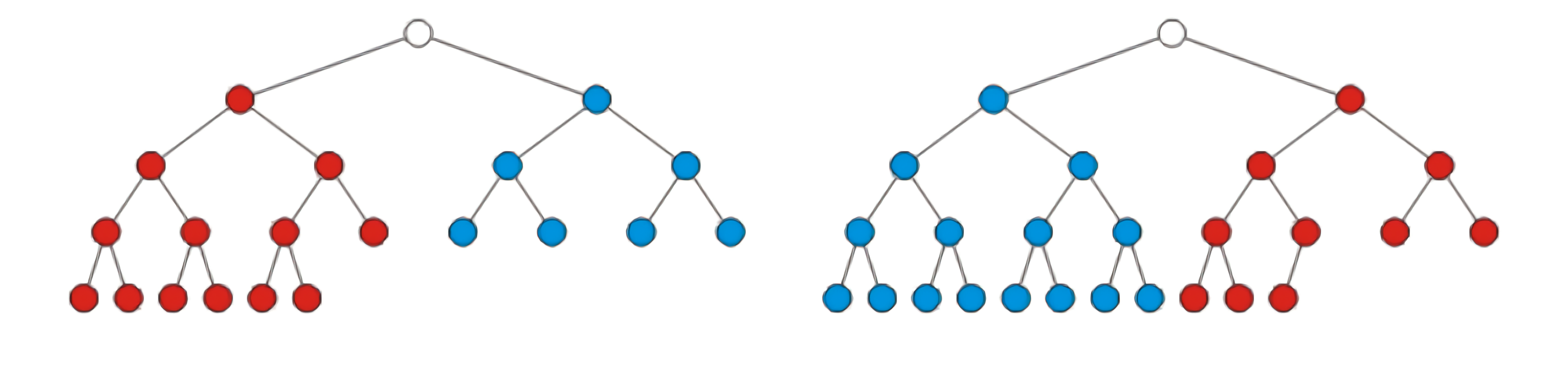
两种complete树
性质
- The height of a complete binary tree with $n$ nodes is is $h=\left \lfloor \lg(n) \right \rfloor $
- We are able to store a complete tree as an array。为什么不是所有的二叉树可以用数组存储,这是因为可能会带来空间上的浪费,特别是当二叉树为链状的时候。
full binary tree
定义
A full binary tree is where each node is:
- A full node, or
- A leaf node
示意图如下,其中绿色点为leaf node,黑色点为full node
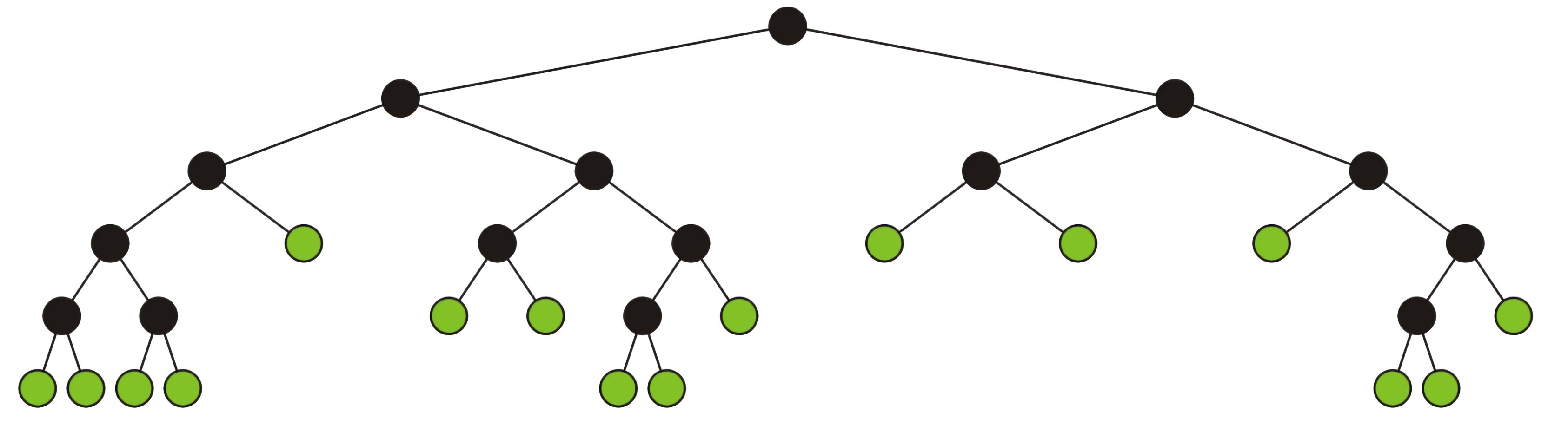
full binary tree
二叉树遍历
二叉树的遍历主要分为三种
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
因此下文将对这三种遍历方式逐个进行讲解
前序遍历
所谓前序遍历,简单来说就是按照“根左右”的顺序遍历。
伪代码
1 | void traverse(TreeNode* root){ |
其实前序遍历可以看做DFS,即广度优先搜索。并且除了用递归,我们可以直接显示地使用栈来模拟递归
1 | void traverse(TreeNode* root){ |
中序遍历
所谓中序遍历,简单来说就是按照“左根右”的顺序遍历。
伪代码
1 | void traverse(TreeNode* root){ |
后序遍历
所谓后序遍历,简单来说就是按照“左右根”的顺序遍历。
伪代码
1 | void traverse(TreeNode* root){ |
层序遍历
一般二叉树中不怎么谈层序遍历,其实它就是BFS,即广度优先搜索,需要借助队列来实现
伪代码
1 | // 每层的顺序是从左到右 |